
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
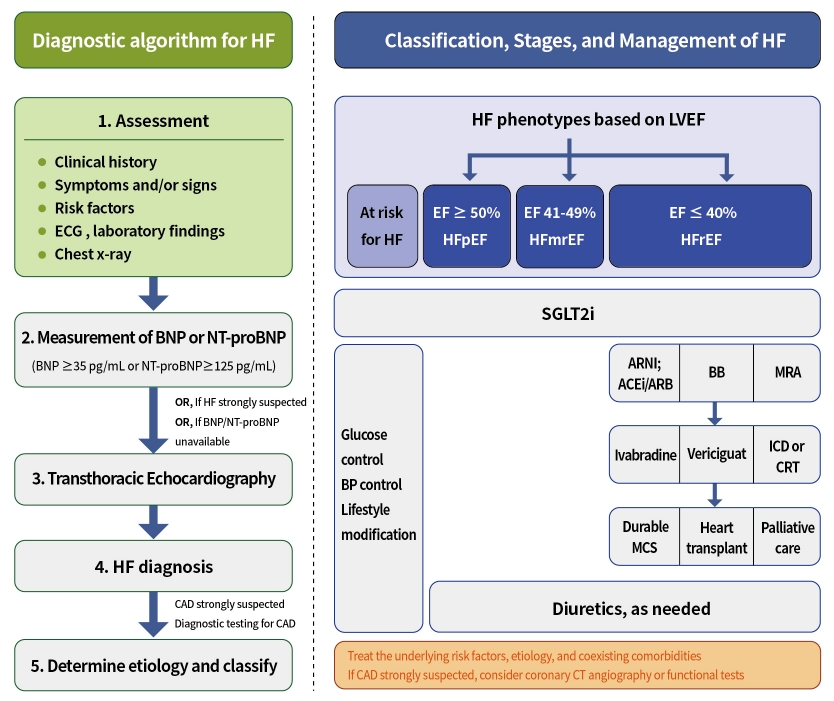
- Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society of Heart Failure
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):10-26. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0420
- 4,336 View
- 411 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for the development of heart failure. Furthermore, the prognosis of heart failure is worse in patients with diabetes mellitus than in those without it. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper management of heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus are important. This review discusses the current criteria for diagnosis and screening tools for heart failure and the currently recommended pharmacological therapies for heart failure. We also highlight the effects of anti-diabetic medications on heart failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Hae Jin Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu Yeon Hur, In-Kyung Jeong, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin versus glimepiride on cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin: The gemi‐heart study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, In‐Chang Hwang, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2181. CrossRef - Optimization of guideline-directed medical treatment for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction
Minjung Bak, Jin-Oh Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(5): 595. CrossRef
- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
- Cardiovascular risk/Epidemiology
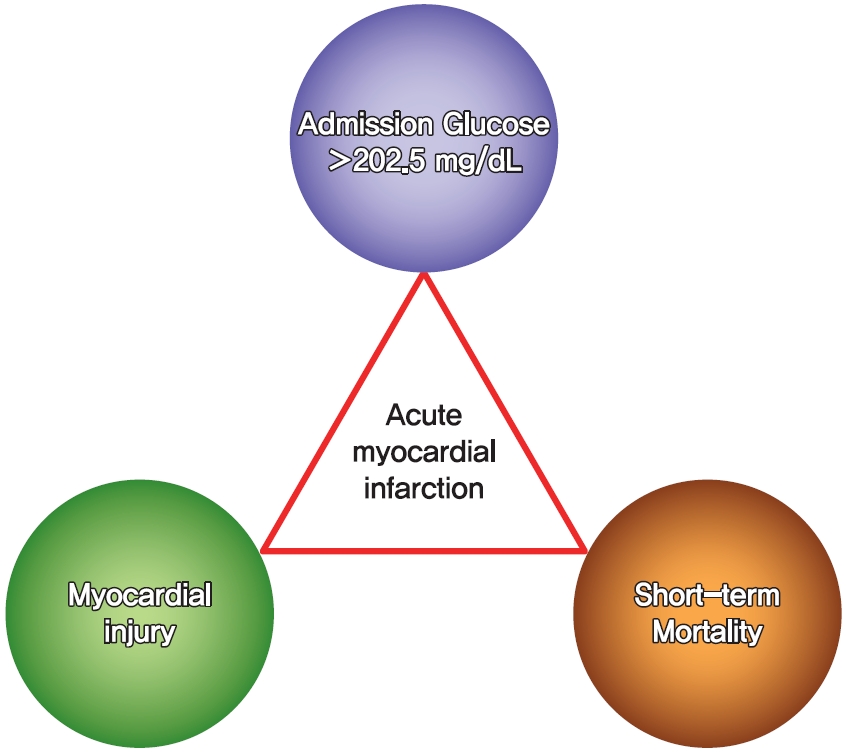
- Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Jae-Wook Chung, Yeong-Seon Park, Jeong-Eon Seo, Yeseul Son, Cheol-Woo Oh, Chan-Hee Lee, Jong-Ho Nam, Jung-Hee Lee, Jang-Won Son, Ung Kim, Jong-Seon Park, Kyu-Chang Won, Dong-Gu Shin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):270-274. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0164
- 5,648 View
- 119 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
This study aimed to determine the impact of dysglycemia on myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction in acute myocardial infarctions (AMIs). From 2005 to 2016, a total of 1,593 patients with AMIs who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention were enrolled. The patients were classified into five groups according to the admission glucose level: ≤80, 81 to 140, 141 to 200, 201 to 260, and ≥261 mg/dL. The clinical and echocardiographic parameters and 30-day mortality were analyzed. The peak troponin I and white blood cell levels had a positive linear relationship to the admission glucose level. The left ventricular ejection fraction had an inverted
U -shape trend, and the E/E' ratio wasU -shaped based on euglycemia. The 30-day mortality also increased as the admission glucose increased, and the cut-off value for predicting the mortality was 202.5 mg/dL. Dysglycemia, especially hyperglycemia, appears to be associated with myocardial injury and could be another adjunctive parameter for predicting mortality in patients with AMIs.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Sang Wook Park, Tae-Hwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Sang-Hak Lee, Jang-Young Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of admission hyperglycemia and all-cause mortality in acute myocardial infarction with percutaneous coronary intervention: A dose–response meta-analysis
Shao-Yong Cheng, Hao Wang, Shi-Hua Lin, Jin-Hui Wen, Ling-Ling Ma, Xiao-Ce Dai
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Basic types of the first-day glycemia in acute myocardial infarction: Prognostic, diagnostic, threshold and target glycemia
Goran Koracevic, Milan Djordjevic
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(3): 614. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:270-4)
Bo-Yeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 787. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:270-4)
Chan-Hee Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 791. CrossRef - The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 977. CrossRef - Effect of Admission Hyperglycemia on Short-Term Prognosis of Patients with Non-ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome without Diabetes Mellitus
Wei Liu, Zhijuan Li, Shiying Xing, Yanwei Xu, Gaetano Santulli
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
- Lifesytle
- Changes in the Quality of Life in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus According to Physician and Patient Behaviors
- Young-Joo Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, Sin-Gon Kim, Dong Hyeok Cho, Chong-Hwa Kim, Chul-Sik Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kyu-Chang Won, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Doo-Man Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):91-102. Published online October 23, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0251
- 5,880 View
- 95 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetes mellitus (DM) is the most common chronic metabolic disorder with an increasing prevalence worldwide. According to a previous study, physicians' treatment patterns or patients' behaviors change when they become aware of the risk for cardiovascular (CV) disease in patients with DM. However, there exist controversial reports from previous studies in the impact of physicians' behaviors on the patients' quality of life (QoL) improvements. So we investigate the changes in QoL according to physicians and patients' behavioral changes after the awareness of CV risks in patients with type 2 DM.
Methods Data were obtained from a prospective, observational study where 799 patients aged ≥40 years with type 2 DM were recruited at 24 tertiary hospitals in Korea. Changes in physicians' behaviors were defined as changes in the dose/type of antihypertensive, lipid-lowering, and anti-platelet therapies within 6-month after the awareness of CV risks in patients. Changes in patients' behaviors were based on lifestyle modifications. Audit of Diabetes Dependent Quality of Life comprising 19-life-domains was used.
Results The weighted impact score change for local or long-distance journey (
P =0.0049), holidays (P =0.0364), and physical health (P =0.0451) domains significantly differed between the two groups; patients whose physician's behaviors changed showed greater improvement than those whose physician's behaviors did not change.Conclusion This study demonstrates that changes in physicians' behaviors, as a result of perceiving CV risks, improve QoL in some domains of life in DM patients. Physicians should recognize the importance of understanding CV risks and implement appropriate management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Spline Longitudinal Multi-response Model for the Detection of Lifestyle-
Based Changes in Blood Glucose of Diabetic Patients
Anna Islamiyati
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - Agriophyllum Oligosaccharides Ameliorate Diabetic Insulin Resistance Through INS-R/IRS/Glut4-Mediated Insulin Pathway in db/db Mice and MIN6 Cells
Shuyin Bao, Xiuzhi Wang, Sung Bo Cho, Yan-Ling Wu, Chengxi Wei, Shuying Han, Liming Bao, Qiong Wu, Wuliji Ao, Ji-Xing Nan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolipid metabolism and liver transcriptomic analysis of the therapeutic effects of pressed degreased walnut meal extracts on type 2 diabetes mellitus rats
Yulan Li, Dan Chen, Chengmei Xu, Qingyujing Zhao, Yage Ma, Shenglan Zhao, Chaoyin Chen
Food & Function.2020; 11(6): 5538. CrossRef - Cause-of-death statistics in 2018 in the Republic of Korea
Hyun-Young Shin, Jin Kim, Seokmin Lee, Min Sim Park, Sanghee Park, Sun Huh
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2020; 63(5): 286. CrossRef
- Spline Longitudinal Multi-response Model for the Detection of Lifestyle-
Based Changes in Blood Glucose of Diabetic Patients
- Corrigendum: Hemorheologic Alterations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Presented with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Kyu-Hwan Park, Ung Kim, Kang-Un Choi, Jong-Ho Nam, Jung-Hee Lee, Chan-Hee Lee, Jang-Won Son, Jong-Seon Park, Dong-Gu Shin, Kyu-Chang Won, Jun Sung Moon, Yu Kyung Kim, Jang-Soo Suh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):254-254. Published online June 19, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0096
- 3,437 View
- 31 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Erythrocytes: Central Actors in Multiple Scenes of Atherosclerosis
Chloé Turpin, Aurélie Catan, Olivier Meilhac, Emmanuel Bourdon, François Canonne-Hergaux, Philippe Rondeau
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(11): 5843. CrossRef - Self-care Efficacy and Health-related Quality of Life among Patients on Primary Treatment for Pulmonary Tuberculosis: The Mediating Effects of Self-Care Performance
Hyun Ju Lee, Jiyoung Park
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(3): 305. CrossRef
- Erythrocytes: Central Actors in Multiple Scenes of Atherosclerosis
- Others
- Hemorheologic Alterations in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Presented with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Kyu-Hwan Park, Ung Kim, Kang-Un Choi, Jong-Ho Nam, Jung-Hee Lee, Chan-Hee Lee, Jang-Won Son, Jong-Seon Park, Dong-Gu Shin, Kyu-Chang Won, Jun Sung Moon, Yu Kyung Kim, Jang-Soo Suh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):155-163. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.155
- 4,269 View
- 41 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Hemorheologic indices are known to be related to vascular complications in variable clinical settings. However, little is known about the associations between hemorheologic parameters and acute myocardial infarction (AMI) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the changes of hemorheologic environment inside of blood using hemorheologic parameters, especially the elongation index (EI) and critical shear stress (CSS) in diabetics with versus without AMI.
Methods A total of 195 patients with T2DM were enrolled. Patients were divided into the study group with AMI (AMI+,
n =77) and control group (AMI−,n =118) who had no history of coronary artery disease. Hemorheologic parameters such as EI and CSS were measured and compared between the two groups.Results The EI was lower (30.44%±1.77% in AMI+ and 31.47%±1.48% in AMI−,
P <0.001) but the level of CSS was higher (316.13±108.20 mPa in AMI+ and 286.80±85.34 mPa in AMI−,P =0.040) in the AMI+. The CSS was significantly related to the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (R 2=0.497,P <0.001) and use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (R 2=0.574,P =0.048).Conclusion Diabetics with AMI resulted in adverse hemorheologic changes with lower EI and higher CSS compared to diabetic subjects without AMI. Evaluation of the hemorheologic parameters may provide valuable supplementary information for managing patients with AMI and T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Alpha-SNAP (M105I) mutation promotes neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells through overactivation of AMPK
Felipe A. Bustamante-Barrientos, Maxs Méndez-Ruette, Luis Molina, Tania Koning, Pamela Ehrenfeld, Carlos B. González, Ursula Wyneken, Roberto Henzi, Luis Federico Bátiz
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Red Cell Distribution Width and Elongation Index in a Cohort of Patients With Juvenile Acute Myocardial Infarction
Gregorio Caimi, Rosalia Lo Presti, Egle Corrado, Maria Montana, Melania Carlisi
Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Zinc improved erythrocyte deformability and aggregation in patients with beta-thalassemia: An in vitro study
Mukaddes Sinan, Ozlem Yalcin, Zeynep Karakas, Evrim Goksel, Nesrin Zeynep Ertan
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2023; 85(1): 1. CrossRef - Improved Erythrocyte Deformability Induced by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Minkook Son, Ye Sung Lee, A Ram Hong, Jee Hee Yoon, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sung Yang
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2022; 36(1): 59. CrossRef - Change of RBC Deformability During Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation
Yu Kyung Kim, Jae Min Lee
Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.2022; 44(2): e329. CrossRef - Hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit and red blood cell count predict major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia
Martine Paquette, Sophie Bernard, Alexis Baass
Atherosclerosis.2021; 335: 41. CrossRef - Erythrocyte deformability reduction in various pediatric hematologic diseases
Yu Kyung Kim, Young Tae Lim, Jang Soo Suh, Jeong Ok Hah, Jae Min Lee
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2020; 75(3): 361. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Variability and Gastric Cancer Risk in Individuals Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
So-hyeon Hong, Eunjin Noh, Jinsil Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Jun A. Kim, You-Bin Lee, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2020; 11(9): e00221. CrossRef - Use of RBC deformability index as an early marker of diabetic nephropathy
Sang Bae Lee, Yu-Sik Kim, Jung Hye Kim, Kahui Park, Ji Sun Nam, Shinae Kang, Jong Suk Park, Sehyun Shin, Chul Woo Ahn
Clinical Hemorheology and Microcirculation.2019; 72(1): 75. CrossRef - Haemorheological and haemostatic alterations in coeliac disease and inflammatory bowel disease in comparison with non-coeliac, non-IBD subjects (HERMES): a case–control study protocol
Zsolt Szakács, Beáta Csiszár, Péter Kenyeres, Patrícia Sarlós, Bálint Erőss, Alizadeh Hussain, Ágnes Nagy, Balázs Kőszegi, Ibolya Veczák, Nelli Farkas, Emőke Bódis, Katalin Márta, Andrea Szentesi, Margit Tőkés-Füzesi, Tímea Berki, Áron Vincze, Kálmán Tóth
BMJ Open.2019; 9(3): e026315. CrossRef - Potential Diagnostic Hemorheological Indexes for Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Hoyoon Lee, Wonwhi Na, Sang Bae Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won, Sehyun Shin
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - PREVALENCE AND FORECASTING OF ALIMENTARY RISK FACTORS AMONG PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
A. V. Ivanenko, R. S. Goloschapov-Aksenov, Dmitry I. Kicha
Hygiene and sanitation.2019; 98(8): 873. CrossRef
- Alpha-SNAP (M105I) mutation promotes neuronal differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells through overactivation of AMPK
- Hexane Extract of
Orthosiphon stamineus Induces Insulin Expression and Prevents Glucotoxicity in INS-1 Cells - Hae-Jung Lee, Yoon-Jung Choi, So-Young Park, Jong-Yeon Kim, Kyu-Chang Won, Jong-Keun Son, Yong-Woon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(1):51-58. Published online February 16, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.1.51
- 4,448 View
- 62 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Hyperglycemia, a characteristic feature of diabetes, induces glucotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells, resulting in further impairment of insulin secretion and worsening glycemic control. Thus, preservation of insulin secretory capacity is essential for the management of type 2 diabetes. In this study, we evaluated the ability of an
Orthosiphon stamineus (OS) extract to prevent glucotoxicity in insulin-producing cells.Methods We measured insulin mRNA expression and glucose-stimulated insulin secretion (GSIS) in OS-treated INS-1 cells after exposure to a high glucose (HG; 30 mM) concentration.
Results The hexane extract of OS elevated mRNA expression of insulin as well as pancreatic and duodenal homeobox-1 of INS-1 cells in a dose-dependent manner. The hexane OS extract also increased the levels of phosphorylated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) in a concentration-dependent manner. Additionally, Akt phosphorylation was elevated by treatment with 100 and 200 µmol of the hexane OS extract. Three days of HG exposure suppressed insulin mRNA expression and GSIS; these expressions were restored by treatment with the hexane OS extract. HG elevated peroxide levels in the INS-1 cells. These levels were unaffected by OS treatment under both normal and hyperglycemic conditions.
Conclusion Our results suggested that the hexane extract of OS elevates insulin mRNA expression and prevents glucotoxicity induced by a 3-day treatment with HG. This was associated with the activation of PI-3K and Akt.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An Updated Review of Ethnobotany, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth
Anandarajagopal Kalusalingam, Dania Najiha Hasnu, Abdullah Khan, Ching Siang Tan, Bama Menon, Venkateshan Narayanan, Khang Wen Goh, Asmuni Mohd Ikmal, Noraini Talip, Poonguzhali Subramanian, Long Chiau Ming
Malaysian Applied Biology.2024; 53(1): 1. CrossRef - Scopoletin protects INS-1 pancreatic β cells from glucotoxicity by reducing oxidative stress and apoptosis
Jae Eun Park, Ji Sook Han
Toxicology in Vitro.2023; 93: 105665. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth. in the Treatment of Diabetes and Its Complications
Qirou Wang, Jia Wang, Nannan Li, Junyu Liu, Jingna Zhou, Pengwei Zhuang, Haixia Chen
Molecules.2022; 27(2): 444. CrossRef - Comprehensive chemical and metabolic profiling of anti‐hyperglycemic active fraction from Clerodendranthi Spicati Herba
Yun Luo, Yue Liu, Quan Wen, Yulin Feng, Ting Tan
Journal of Separation Science.2021; 44(9): 1805. CrossRef - Short-Term Protocols to Obtain Insulin-Producing Cells from Rat Adipose Tissue: Signaling Pathways and In Vivo Effect
Krista Minéia Wartchow, Letícia Rodrigues, Lucas Zingano Suardi, Barbara Carolina Federhen, Nicholas Guerini Selistre, Carlos-Alberto Gonçalves, Patrícia Sesterheim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(10): 2458. CrossRef - Understanding glycaemic control and current approaches for screening antidiabetic natural products from evidence-based medicinal plants
Chintha Lankatillake, Tien Huynh, Daniel A. Dias
Plant Methods.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - 50% Ethanol extract of Orthosiphon stamineus modulates genotoxicity and clastogenicity induced by mitomycin C
Dhamraa Waleed Al-dualimi, Aman Shah Abdul Majid, Sarah Furqan Faisal Al-Shimary, Amal Aziz Al-Saadi, Raghdaa Al Zarzour, Muhammad Asif, Chern Ein Oon, Amin Malik Shah Abdul Majid
Drug and Chemical Toxicology.2018; 41(1): 82. CrossRef - Can Tea Extracts Exert a Protective Effect Against Diabetes by Reducing Oxidative Stress and Decreasing Glucotoxicity in Pancreatic β-Cells?
Heeyoung Chae, Patrick Gilon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(1): 27. CrossRef
- An Updated Review of Ethnobotany, Ethnopharmacology, Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Activities of Orthosiphon stamineus Benth
- Letter: Lack of Association between Serum Cystatin C Levels and Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:95-100)
- Kyu-Chang Won
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(3):207-208. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.207
- 2,596 View
- 22 Download

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





